The project is based on the box constraint of portfolio efficient frontier construction with different constraint methods used on simulated resampling data to find the relationship between constraints and minimum variance or tangent portfolio volatility range calculated from the resamples. The main methodologies are multivariate t-distribution fitting and bootstrapping based on estimated parameters. Data source is the daily return on 9 stocks in recent 15 years.
Main findings are as follows:
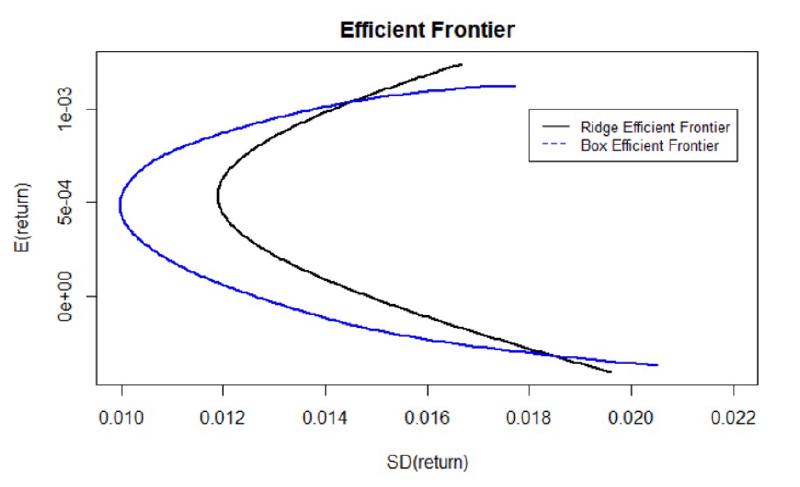
- Ridge constraint is tighter than box constraint in efficient frontier value range. The minimum variance it can reach is larger than that of box constraint situation.
- For minimum variance portfolios, box constraints have smaller value and range than ridge constraint. That is, when using box constraints on the sample to calculate minimum variance portfolio, it is more likely to be a more precise estimation of true minimum variance.
- For tangent portfolios, ridge constraint reaches the minimum volatility and range. Also, tangent portfolios are more largely influenced by the change of constraints.